Home / GCP / GCP Training / Ref - Kubernetes and Containers
Contents
Overview
Containers deliver a solution that sits somewhere between IaaS (GCE) and PaaS (App Engine).
GCE - VMs - An App runs on an OS running on a Hypervisor running on HW.
App Engine - An App runs on a service delivering Data, Cache, Storage, DBs, NW etc - very abstracted from the HW.
Containers - An App runs in a container which provides an OS delivered by the container engines which utilises the HW OS.
Kubernetes manages the execution of containers over a cluster of nodes (running on servers).
Cloud Build is a GCP container build tool.
Docker
Docker File: (pg_server)
FROM ubuntu:18.10
RUN apt-get update -y &&\
apt-get install -y python-pip python3-dev
COPY requirements.txt /app/requirements.txt
WORKDIR /app
RUN pip3 install -r requirements.txt
COPY . /app
ENTRYPOINT ["python3", "app.py"]
> docker build -t pg_server .
> docker run -d pg_server
Kubernetes
> gcloud container clusters create k1
Pods
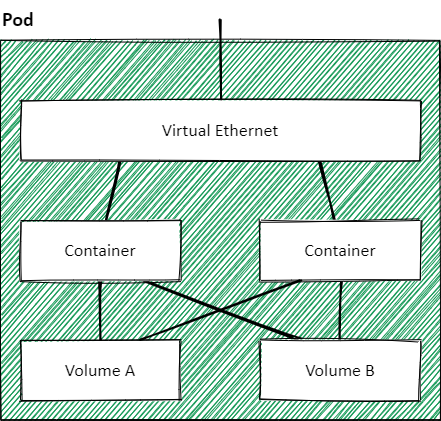
A Pod has a unique IP address.
> kubectl run nginx --image=nginx:1.15.7
> kubectl get pods
> kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 --type=LoadBalancer
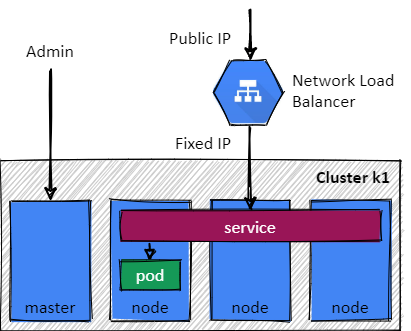
A service groups pods together with a single point of access (a fixed IP).
> kubectl get services
Scaling is easy.
>kubectl scale nginx --replicas=3
Auto scale when CPU hits 80%.
kubectl autoscale nginx --min-10 --max=15 --cpu=80
Kubernetes adopts a Declarative Approach
Uses config files and not commands.
kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
kubectl get replica
kubectl get pod
kubectl get deployments
kubectl get services
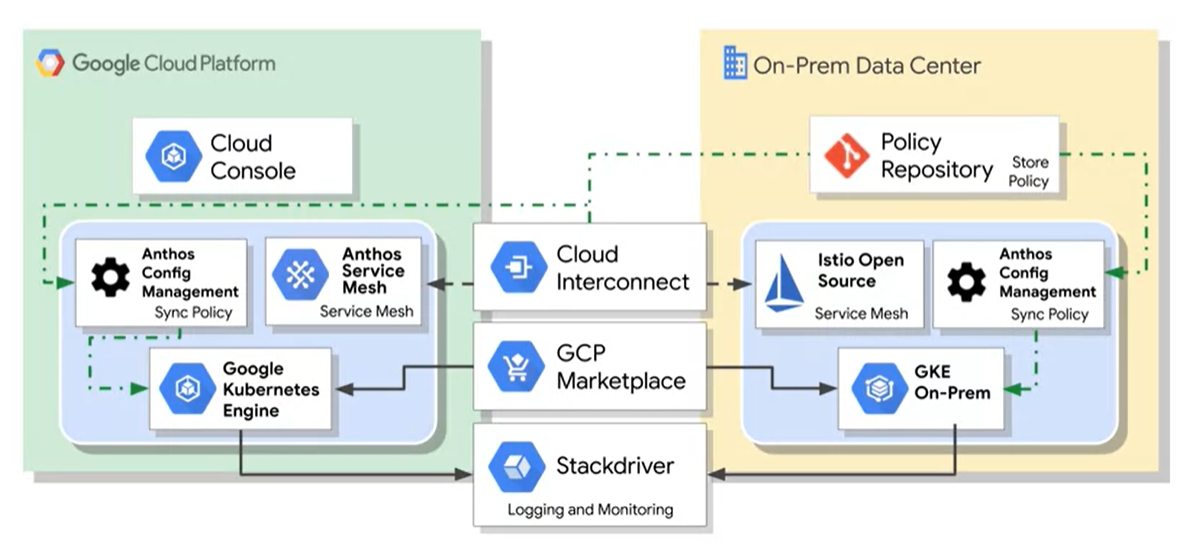
Anthos
Hybrid / Multi Cloud
Kubernetes with GKE on prem`.
Both can read containers from the GCP Marketplace.
This page was generated by GitHub Pages. Page last modified: 22/12/04 17:45